
ZhETF, Vol. 169,
No. 2,
p. 212 (February 2026)
(English translation - JETP,
Vol. 142, No. 2,
February 2026
available online at www.springer.com
)
Magnetic Resonance in Nanogranular Composites: Observation and Properties of «Double Quantum» Excitations in Ferromagnetic Particles
Drovosekov A.B., Dmitrieva M.Yu., Sitnikov A.V., Nikolaev S.N., Rylkov V.V.
Received: December 8, 2025
DOI: 10.7868/S3034641X26020088
Films of metal-insulator nanogranular composites (CoFeB)x(Al2O3)100-x and (CoFeB)x(SiO2)100-x with different content of metal ferromagnetic phase CoFeB (x\approx 20-60 at.%) are investigated by electron spin resonance. The experiments are carried out in a wide range of frequencies (f=7-80 GHz) and temperatures (T=4.2-360 K) at different orientations of the magnetic field (up to 24 kOe) with respect to the film plane. Besides the conventional ferromagnetic resonance signal, the experimental spectra contain a weak additional absorption peak which is characterized by a double effective g-factor g eff\approx 4 and demonstrates a number of other unusual properties. The appearance of such a peak in the resonance spectra can be explained in the framework of the quantum mechanical «giant spin» model by the excitation of «forbidden» («double quantum») transitions in magnetic nanogranules with a change of the spin projection 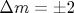 . Here we study the applicability of this model to explain anomalous behavior of the g eff\approx 4 resonance peak, as well as discuss a classical interpretation of the observed phenomena. In particular, the influence of dipolar fields in the films on the frequency-field dependencies for the «double quantum» absorption peak is of interest. Keywords:} magnetic nanoparticles, superparamagnetism, electron spin resonance . Here we study the applicability of this model to explain anomalous behavior of the g eff\approx 4 resonance peak, as well as discuss a classical interpretation of the observed phenomena. In particular, the influence of dipolar fields in the films on the frequency-field dependencies for the «double quantum» absorption peak is of interest. Keywords:} magnetic nanoparticles, superparamagnetism, electron spin resonance
|
|